Air Emissions

Climate Change has brought air emissions into focus of the strategic planning and decision making of all the countries and companies around the world. Steel industry, which is associated with generation of huge amount of a wide variety of polluting emissions to air like carbon dioxide and methane, is required to work towards controlling its green house gas (GHG) emissions. JSW Steel being a part of a carbon intensive sector has taken conscious efforts to siege every opportunity to reduce the carbon footprint of its production process. JSW has implemented all the best available technologies in the world for Air Emission abatement in its operations. JSW has and will always strive to achieve the lowest emissions in the industry and comply with the INDC’s of the Indian Government in order to align itself to the goals of the Paris Agreement.
SDG Mapping of JSW Steel’s Initiatives & Projects
SDG 13: Climate Change
We conducted natural capital impact assessment to assess the invisible impacts (both positive and negative) on nature or natural capital. Natural Capital Impacts are calculated (quantity and economic valuation) across six KPIs - namely, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, air pollution, water consumption, water and land pollution, waste generation, and land use change.
The assessment study was carried out to quantify and value the natural capital impacts of JSW’s direct operations, upstream indirect impacts, avoided impacts due to waste recycling, selling of co-products, etc., and impacts due to biological carbon sequestration. The study covered JSW’s operations at 3 Integrated Steel Plants for which direct and upstream impacts were estimated by deploying standardised methodologies. We further quantified the direct or indirect impacts in terms of financial implications to get a holistic understanding of JSW’s sustainability performance. The assessment considered evaluation of internal and external stakeholders such as environment, society, consumers, and suppliers.
In iron and steel production, there are various sources of emissions including stationary source of emissions from boilers, coke, coal, carbonate fluxes, consumption of purchased electricity, heat or steam, upstream transportation, etc., and mobile combustion (on-site transportation, transportation of raw materials/products/waste and intermediate products). There are also fugitive emissions, process emissions, and hazardous air pollutants. Air pollutants of particular concern are Sox and NOx, as well as particles such as soot and dust, which are released during the production process from operations. The release of emissions has long-term environmental, health, and economic impacts. Expansion of operations can further lead to an increase in greenhouse gases.
To mitigate the negative impacts of GHG emissions including air emissions, we have undertaken various interventions at our operations, resulting in reduced emissions. Examples include the reduction of emissions by 1,84,924 tCO2 due to the implementation of a 60 MW waste heat recovery coke dry quenching system at one of our captive power plants in Dolvi. In addition to this, we released our first Climate Action Report in line with four thematic areas of the TCFD: Governance, Strategy, Risk Management, and Metrics and Targets. The report can be accessed on our website.
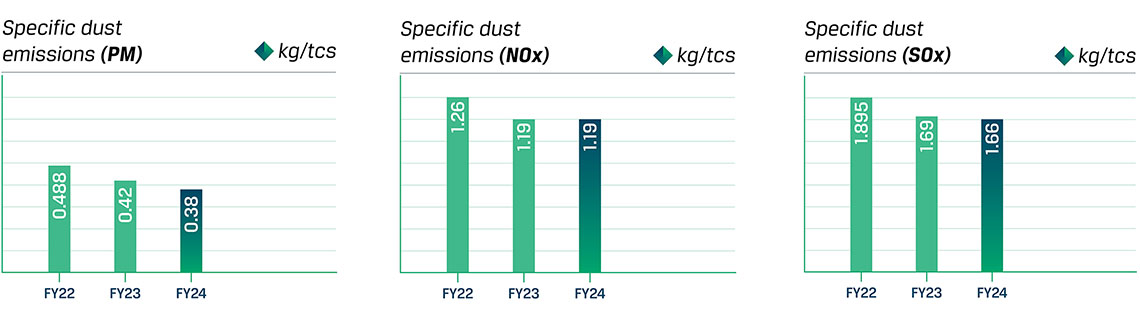
We have further implemented a range of policies and strengthened our practices to prevent, control, and mitigate our air emissions. Our focus is on reducing both point-source (like stack emissions) and non-point source (like fugitive emissions) pollution. For instance, the existing air pollution control measures of one of our sinter plants in Salem were replaced with an ESP, which resulted in the reduction of dust emission by 62.5%, and the paving of mud roads using in-house paver blocks resulted in the reduction of fugitive emissions by 89%. Details related to various initiatives and interventions can be found in our Integrated Report. During the year, there was a total reduction of PM emissions by 0.04 kg/tcs (~9.52% reduction), and Sox emissions by 0.03 kg/tcs (~1.77% reduction).
With the objective of minimizing our impact on the environment, we conducted Cradle to Gate life cycle assessment of products which contribute to 100% of our total turnover.
To maintain the air quality and limit the fugitive dust, good practices should be implemented to mitigate direct impact on the air quality as well as indirect impact on the human health of the people in the vicinity due to the activities undertaken in the construction, maintenance, and decommissioning phases. However, with requisite mitigation efforts, the impact can be minimized and made negligible.
- It is possible for the steel industry to reduce its GHG emisions by taking the following routes -
- Reduction of steel consumption – Development of such prodcuts which fulfill customer requirements in less quatity. JSW is into production of speciality steel that is used in manufacturing of energy-efficient motors.
- Retrofitting existing technologies to make them more energy efficient and less carbon intensive – JSW has invested in certain technologies like installation of BF gas holder, top-pressure recovery turbine for BF, hot stove waste heat recovery, installation of energy monitoring and management systems, coke oven waste heat recovery boiler, LD converter dry Gas Cleaning Plant (GCP) and gas holder along with LD convertor waste heat recovery boiler.
- Using alternative to carbon intensive blast furnace process – JSW produces crude steel through electric arc furnace which has a very low CO2 emission intensity. If renewable energy is used in this process, the figure comes down to zero. Other technologies for drastic GHG emission reduction include – utilization of H2 in blast furnace as fuel, carbon capture and storage/utilization etc. But these are still under pilot run or at lab scale testing phase.
- Scrap Steel recycling – Through melting of scrap steel to produce steel again, we could produce steel with very low GHG emissions. Currenlty, JSW utilizes 4% of scrap steel in its operations but is planning to increase this figure upto 20% in order to cut down GHG emisisons.
- JSW is also working towards the implementation of Internal Carbon Pricing to place a monetary value on greenhouse gas emissions as a strategy to manage climate-related business risks and prepare for a transition to a low-carbon economy.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- JSW Steel is shifting towards better technology and processes to reduce Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions for every tonne of steel produced. Over the years, a number of initiatives have been taken to improve the energy efficiency and reduce GHG emissions across the manufacturing units.
- Pipe conveyor has been commissioned to transport iron ore from the mines to Vijaynagar Works. This has reduced truck movements significantly and a reduction of 3.86 kg CO2/t of ore transport is expected. More details on the project can be found in the Resource Framework
- Dry fog systems installed at 105 junction houses for fugitive emission control.
- More than 3 km of wind curtains laid at raw material handling area.
- Installation of scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators and bag filters for emission control.
- Continued focus on conservational initiatives and incorporation of new technologies that can reduce environmental footprint. JSW’s upcoming goal is to make emissions compliant, not just with the local regulations, but also with European standards.
- With a mission to set a benchmark for other steel plants with regard to carbon footprint reduction and emissions, the Company is investing extensively in green belt development through tree plantation in and around the plants to enable carbon dioxide sequestration and derive other benefits like dust control and better landscape.
- JSW has sought various technologies to strengthen the function of Dust Extraction systems in Vijaynagar Plant. 13 new dedusting systems were commissioned in FY19 to reduce 150 dust sources/transfer point emissions. To tackle road emissions, rotating sprinklers were installed along with the usage of road sweeping machine for road cleaning purpose. Reduction of dust generation due to truck movement inside the plant was carried out by installation of Tyre washing unit.
- Through R&D, JSW Steel developed a process for reduction of NOx emission in sinter making.
MEROS (Maximised Emission Reduction of Sintering) System -
- Particulate Matter (PM), SOx and NOx are pollutants that can have severely detrimental effects on local ecosystems, air quality, habitats, agriculture, and human and animal health.
- At JSW Steel, we are committed to preventing, abating and mitigating our emissions to air and have dedicated policies addressing point (stack) and non-point (fugitive) source emissions. In order to contain the emissions, we have put in place systems, policies and interventions to maintain our emissions under the statutory limits.
- To achieve a better compliance and adhering to our environmental commitment, we installed the MEROS (Maximised Emission Reduction of Sintering) system to treat process gases of Sinter Plant 4 at Vijayanagar Works.
- The installation of this state-of-the-art, globally recognised system helps us maintain emissions at less than 10 mg/Nm3.
Air emission trends of JSW Steel
JSW discloses the sustainability related information in its integrated/sustainability reports which can be found here.
